Sleep and Mental Health: The Vital Link You Cannot Ignore
Poor sleep does more than make you tired it affects mood, focus, and even long-term mental health. From anxiety and depression to physical illness, sleep problems can disrupt your whole system. Learn how integrative psychiatry approaches evaluation, treatment, and prevention to restore restful nights and emotional balance.
Moving Toward Mental Health: The Science, Strategy, and Soul of Exercise
Regular movement does more than strengthen muscles or burn calories. It rewires the brain, elevates mood, calms the nervous system, and reconnects us with ourselves. Backed by neuroscience and grounded in lived experience, exercise has emerged as one of the most powerful tools we have for improving mental health. Whether you're walking, lifting, dancing, or stretching, every step is a step toward healing.
The Patterned: How the Self Learns to Survive
Our identities are shaped not just by who we are, but by what we’ve had to become. In this blog, we explore the patterned layer of self; how roles, habits, and adaptations form in response to life’s challenges, and how those same patterns can be gently reworked toward greater coherence, freedom, and healing.
Nourishing the Mind: How Nutrition Influences Mental Health
In a world where mental health care often defaults to medication and talk therapy, we’re overlooking a powerful tool already on our plates. Nutrition profoundly shapes the brain from neurotransmitter synthesis and inflammation to gut health and mood regulation. This blog explores the science, evidence, and practical steps behind nutritional psychiatry, showing how targeted dietary changes can enhance mental wellness across conditions like depression, anxiety, ADHD, and more. Whether you're a practitioner or an individual seeking healing, nutrition offers a vital, and often missing, piece of the puzzle.
The Symbolic: The Architecture of Meaning
The symbolic layer of experience is where emotion finds image and the inner world begins to speak. In this blog, we explore how language, metaphor, and imagination become tools of coherence and how restoring the symbolic can help us transform what once overwhelmed us into meaning we can carry, shape, and heal.
Reclaiming the Soul in Psychiatry: The Vital Role of Spirituality in Mental Health
Spirituality is not an escape from reality but a way of engaging it more deeply. It helps transform raw emotional experience into symbolic meaning, supporting the restoration of coherence across the self. Whether through silence, story, or sacred practice, spirituality invites us back to wholeness not by erasing our pain, but by helping us hold it within a larger frame of purpose and connection.
The Sensorial: Touching the Ground of Being
Long before we can speak or think, the body is already communicating. The sensorial layer of human experience (woven through breath, skin, tone, and rhythm) is our first language. In this blog, we explore how the sensorial forms the ground of the self, how it holds both vulnerability and wisdom, and how simple, embodied practices can help us return to its quiet intelligence.
The Loneliness Epidemic: Understanding the Depths and Finding Our Way Back
Loneliness is no longer just a personal concern; it is a public health crisis with deep physiological, emotional, and social consequences. As new research reveals the widespread nature of this epidemic, it becomes clear that healing loneliness requires more than quick fixes. It demands a return to the Self, a reweaving of community, and a holistic approach to care that honors the complexity of human connection.
Returning to the Unitive: The Ground We Never Left
Beneath all the layers we call identity (beneath sensation, thought, and story) there is a deeper presence that holds it all. This blog explores how we lose contact with this unitive ground, how to return to it, and why remembering it may be the most important step in healing. With practical strategies, videos, and a quiet invitation home, this post offers a path back to the self you never truly left.
Technology in mental health: Apps, wearables, and AI
Digital tools are rapidly reshaping mental health care. From smartphone apps that deliver cognitive behavioral therapy to wearable devices that track subtle physiological signals of stress, these technologies offer new ways to expand access, personalize interventions, and even predict crises before they happen. As artificial intelligence powers chatbots and predictive algorithms, we find ourselves on the edge of a future where mental health support is more proactive, responsive, and woven into daily life. Yet the promise of these innovations must be balanced with thoughtful attention to evidence, ethics, and the irreplaceable role of human connection.
Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy: Where Are We Now and Where Are We Headed?
Psychedelic-assisted therapies using MDMA, psilocybin, and ketamine are reshaping the landscape of mental health care. From groundbreaking studies on PTSD and depression to emerging explorations of end-of-life anxiety and addiction, these treatments promise more than just symptom relief—they invite a deeper engagement with meaning, memory, and human connection. While not without risks or unanswered questions, this new frontier blends neuroscience with the profound terrain of inner experience, offering hope for those whom traditional approaches have left behind.
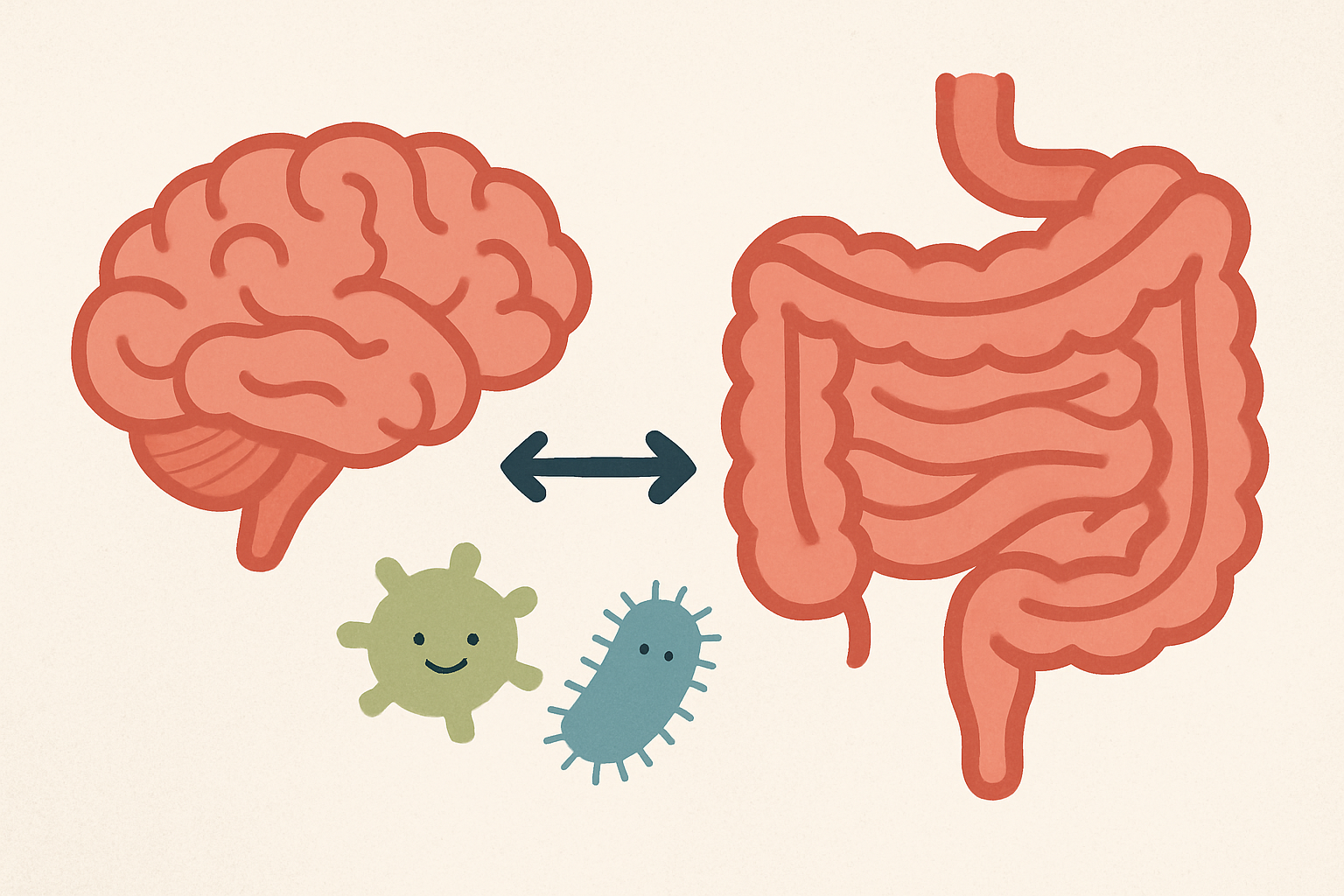
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Key to Psychiatric Wellness
The gut-brain axis is a powerful connection between gut health and mental well-being. An imbalanced gut microbiome, due to conditions like dysbiosis or SIBO, can contribute to psychiatric symptoms such as anxiety and depression. Functional tests like GI MAP and GI Effects help identify underlying gut issues, and addressing these imbalances through diet, probiotics, and targeted treatments can significantly improve mental health. Supporting the gut not only enhances digestion but also promotes mood stability, cognitive function, and overall wellness.
Inflammation and Mental Health: The Hidden Link Behind Depression and Psychosis
Emerging research reveals that chronic low-grade inflammation may quietly fuel conditions like depression and psychosis. Elevated markers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) have been linked to a reduced response to common antidepressants, suggesting that inflammation could undercut traditional treatments. Fortunately, integrative strategies—including nutritional interventions, targeted supplements, regular exercise, and mind-body practices—offer promising ways to lower inflammation and support mental health. By working with an integrative psychiatry specialist, individuals can explore how these factors uniquely interact in their lives and develop a personalized plan that addresses both mind and body.